Hi...
Let's go through some factors about Python Variables in this blog
1. What variables are?
2. Create our first variables in Python
3. Learn about variable " type() "
So let's get started
Well to understand easily we can consider Variable as a box where we can store data. Data can be of any type such as text, images, video, audios, etc.
Now, the variable contains two things :
1. Name
2. Value
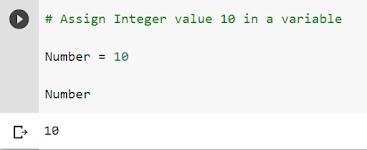
A) Assign " Integer type " value in the variable name Number.
here "Number" is the variable name and the value assigned in it is "10" 👇.
C). Now, We can assign "Float type " data on the same variable
let's check the type of value stored in our variable "Number"
How??
Yea!... you got it right it's now time to use " type( ) " keyword :👇👇
Important Points :
#1. Python variables are case sensitive means variable name "Number" is different from "number".
#2. Python variables are Dynamically typed variable means there is no need to define a variable type like int, float, char, etc before assigning value. But in another languages like C, C++, Java, etc we need to define data type before assigning any value in the variables. C, C++, Java are the statically typed() whereas python is Dynamically typed.
#3. The last value stored is retained in the variable.
Review :
1. Variables are like boxes that store data.
2. Variables can be defined as - variable = value
3. In Python, Variable type can be changed Dynamically.
4. Use the type() variable to get variable type.