Saturday, May 1, 2021
Fundamentals of RS-422: Serial Data Standard (Basics)
Thursday, April 29, 2021
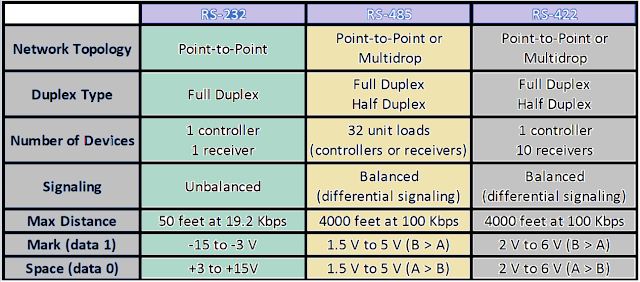
RS-232 STANDARDS, PIN DETAILS, BAUD RATE AND CABLE LENGTH
RS-232 INTERFACE
Communication Standards
Maximum Baud Rate and Cable Length
3. Moxa UPort 1110 1 Port RS232 to USB Converter 2.0 Adapter
4. DTECH USB to RS422 RS485 Serial Port Converter Adapter Cable with FTDI Chip Supports Windows 10, 8, 7, XP and Mac (1.2m)
5. RS232 to RS485 / RS422 Serial Communication Data Converter Adapter Mini-Size
Wednesday, April 28, 2021
Arduino UNO for Middle school, High school, and University Students
ARDUINO UNO
The Arduino UNO is the perfect board for beginners who want to learn about electronics and programming. The UNO is the most stable board you can start with if this is your first time tinkering with the platform. The Arduino UNO is the most famous and well-documented board in the Arduino family.
FUTURE ENGINEERS, SCIENTISTS AND ARTISTS SHOULD BE EMPOWERED
Arduino Education develops the next wave of STEAM services to support students as they progress through middle school, high school, and university.
Arduino Uno R3
Arduino Uno R3 Specifications
The Arduino Uno R3 board includes the following specifications.
- Microcontroller ATmega328P
- Input voltage span from 7V to 12V
- The operating voltage of the Arduino is 5V
- Digital input and output pins
- Analog Input pins
- DC Current used for 3.3V Pin is 50 mA
- DC Current for each I/O Pin is 20 mA
- SRAM is 2 KB
- ROM Memory is 32 KB
- boot loader memory 0.5 KB
- EEPROM is 1 KB
- In-Built LED
- The clock speed is 16 MHz
- Arduino board weight is ~25 g
- Dimensions of the Board are 68.6 mm X 53.4 mm
The Arduino Uno R3 board includes the following specifications.
- Microcontroller ATmega328P
- Input voltage span from 7V to 12V
- The operating voltage of the Arduino is 5V
- Digital input and output pins
- Analog Input pins
- DC Current used for 3.3V Pin is 50 mA
- DC Current for each I/O Pin is 20 mA
- SRAM is 2 KB
- ROM Memory is 32 KB
- boot loader memory 0.5 KB
- EEPROM is 1 KB
- In-Built LED
- The clock speed is 16 MHz
- Arduino board weight is ~25 g
- Dimensions of the Board are 68.6 mm X 53.4 mm
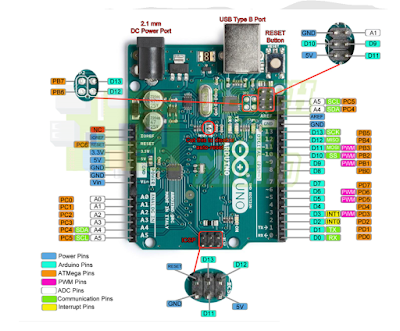
Arduino UNO Pinout Diagram
Digita Channel
Analog Channel
Power Pins
3. UNO Robotics Kit compatible with Arduino IDE
4. Multipurpose Starter Kit for Arduino IDE- NODEMCU (IOT) - Robotics For Beginners
5. Quad Store LEVEL-2 kit with RFID and bluetooth compatible with Arduino IDE and Uno R3
Saturday, October 10, 2020
Python variable
Hi...
Let's go through some factors about Python Variables in this blog
1. What variables are?
2. Create our first variables in Python
3. Learn about variable " type() "
So let's get started
Well to understand easily we can consider Variable as a box where we can store data. Data can be of any type such as text, images, video, audios, etc.
Now, the variable contains two things :
1. Name
2. Value
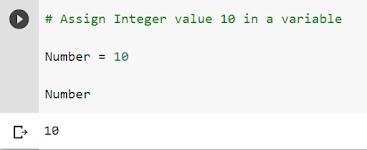
A) Assign " Integer type " value in the variable name Number.
here "Number" is the variable name and the value assigned in it is "10" 👇.
C). Now, We can assign "Float type " data on the same variable
let's check the type of value stored in our variable "Number"
How??
Yea!... you got it right it's now time to use " type( ) " keyword :👇👇
Important Points :
#1. Python variables are case sensitive means variable name "Number" is different from "number".
#2. Python variables are Dynamically typed variable means there is no need to define a variable type like int, float, char, etc before assigning value. But in another languages like C, C++, Java, etc we need to define data type before assigning any value in the variables. C, C++, Java are the statically typed() whereas python is Dynamically typed.
#3. The last value stored is retained in the variable.
Review :
1. Variables are like boxes that store data.
2. Variables can be defined as - variable = value
3. In Python, Variable type can be changed Dynamically.
4. Use the type() variable to get variable type.
Great, enjoy practising till next blog comes☺...
Sunday, October 4, 2020
Python Boolean Operations
Python Boolean Operations: and, or, not
Boolean operators such and, or, and not are also called logical operators.
" and " and " or "operators requires two variables whereas " not " operators need only one variable.
1. "and " operator test example :
It is interesting to know that "and" is a short-circuit operator, it checks both the arguments if both the operands are true or both are false then it returns true. Whereas if any one of the operands is true and other operands are false then it returns false.
2. "or " operator test example :
Like "and" the "or" is also short-circuit operator, it also checks both the argument if any operand is true it returns true. Whereas, if all operands are false then it returns false.
x= 5
y=10
print(x);
print(y);
if (x>10 or y>12):
print("true")
else:
print("false")
3. " not " operator test example :
This operator is also called inverter operator which actually clarifies it's nature or function. It just provides the inverted output. Means if an operand is true then it returns false and vice-versa. It requires only one operand.
# boolean "not" operator test program
x= 5
y=10
print(x);
print(y);
if not (x > 10) :
print("true")
else:
print("flase")